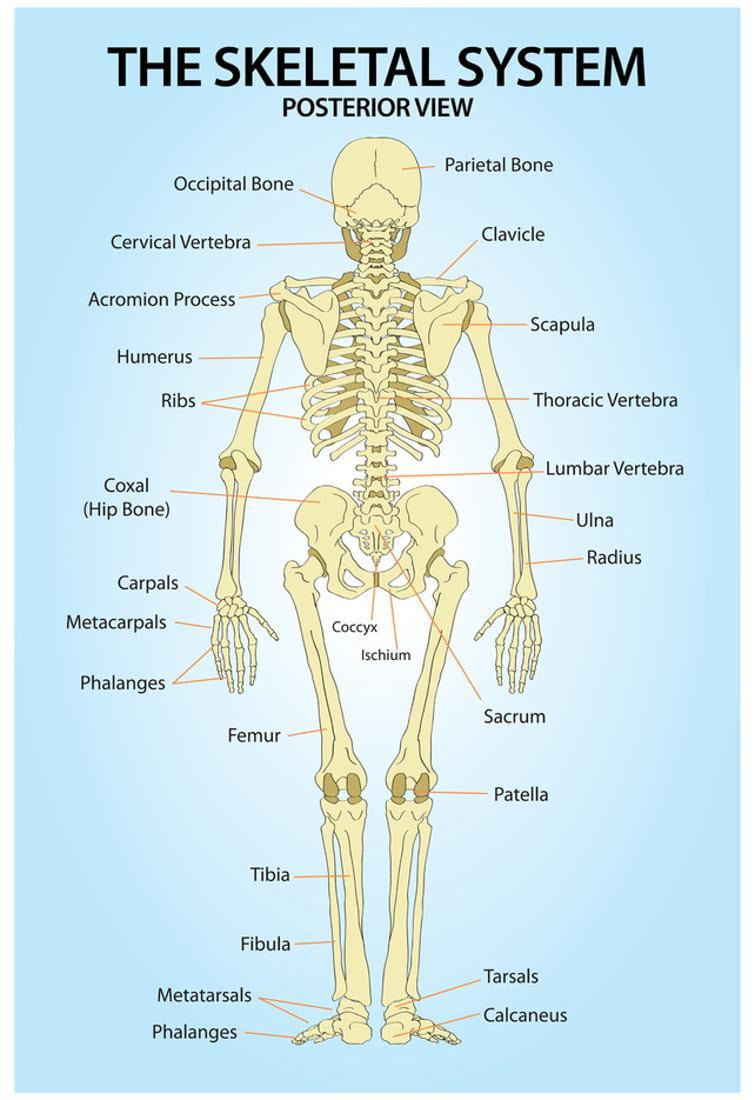
Skeletal System Posterior View Anatomy Print Poster 13x19
Labeling Exercises. Skeleton-Anterior View. Skeleton-Posterior View. Lower Skeleton. Upper Skeleton-Anterior View.
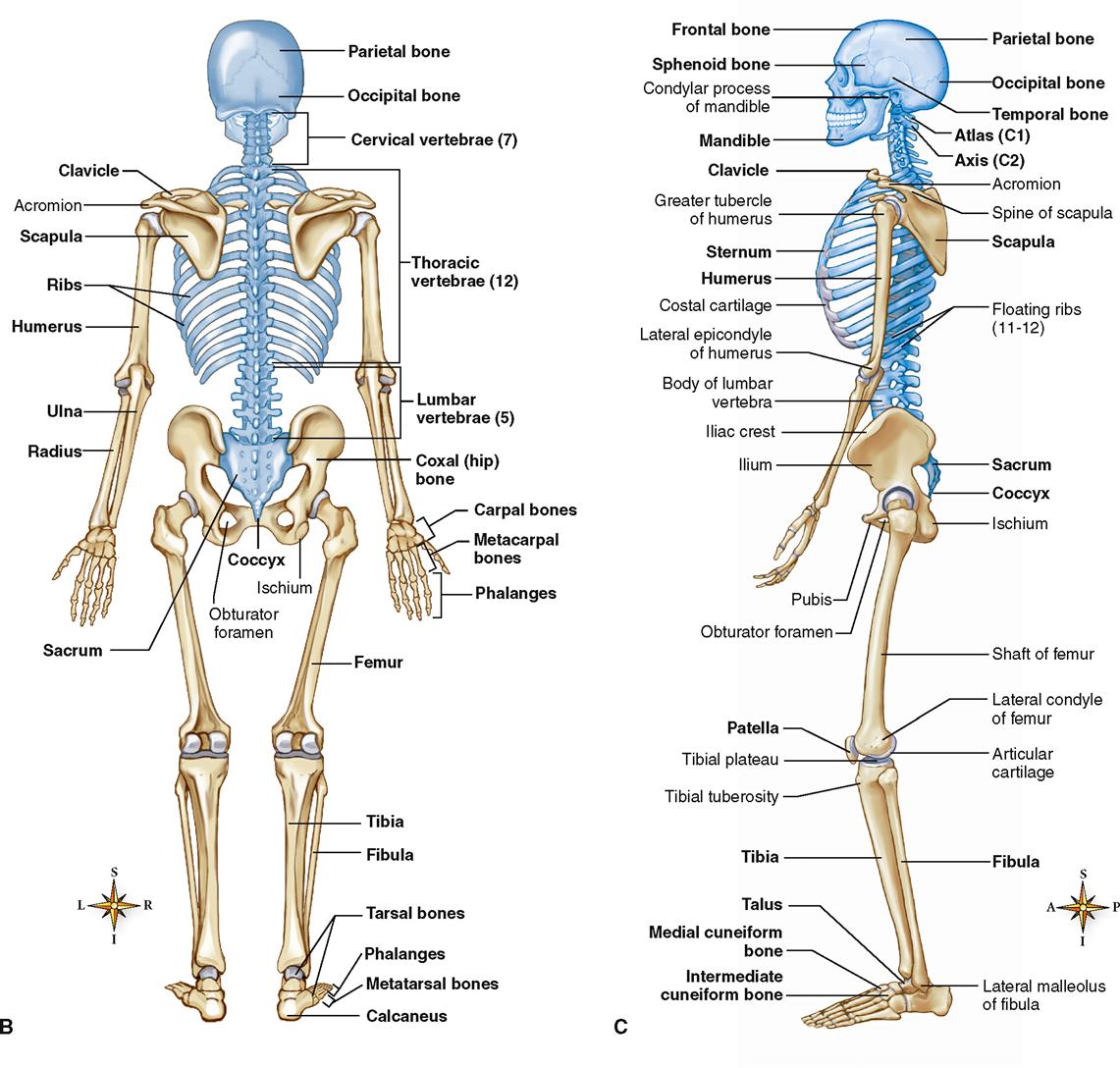
Skeletal System Basicmedical Key
6.1 Skeleton: Overview (See page(s) 84) Name at least five functions of the skeleton. Explain a classification of bones based on their shapes. Describe the anatomy of a long bone. Describe the growth and development of bones. Name and describe six types of fractures, and state the four steps in fracture repair. 6.2 Axial Skeleton (See page(s) 89)
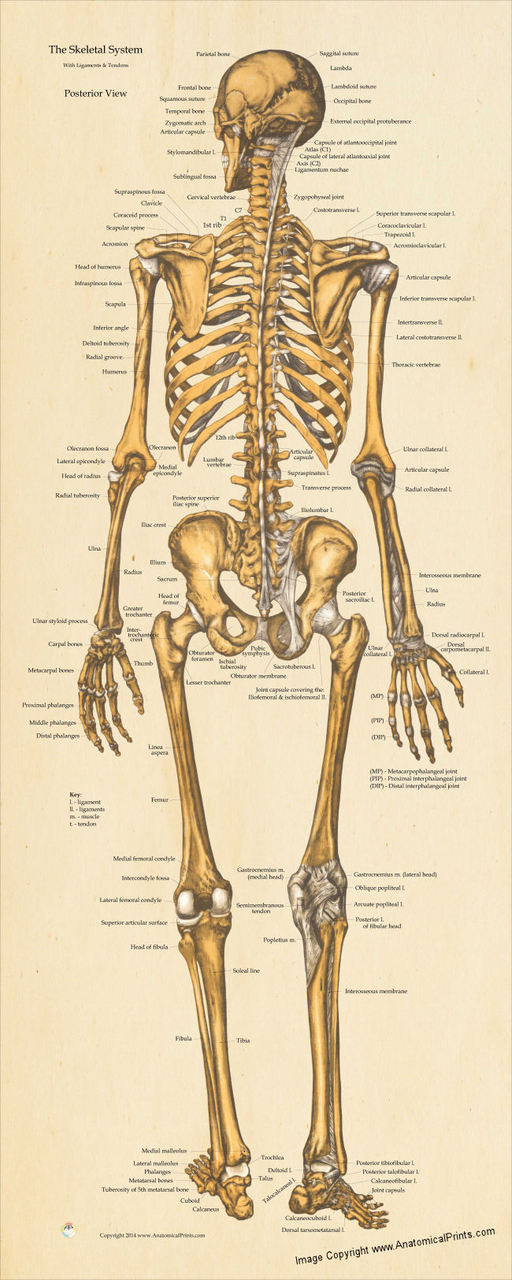
Skeletal System Posterior View Poster Clinical Charts and Supplies
The Skeletal System Explore the skeletal system with our interactive 3D anatomy models. Learn about the bones, joints, and skeletal anatomy of the human body. By: Tim Taylor Last Updated: Jul 29, 2020 2D Interactive NEW 3D Rotate and Zoom Anatomy Explorer HEAD AND NECK CHEST AND UPPER BACK PELVIS AND LOWER BACK ARM AND HAND LEG AND FOOT
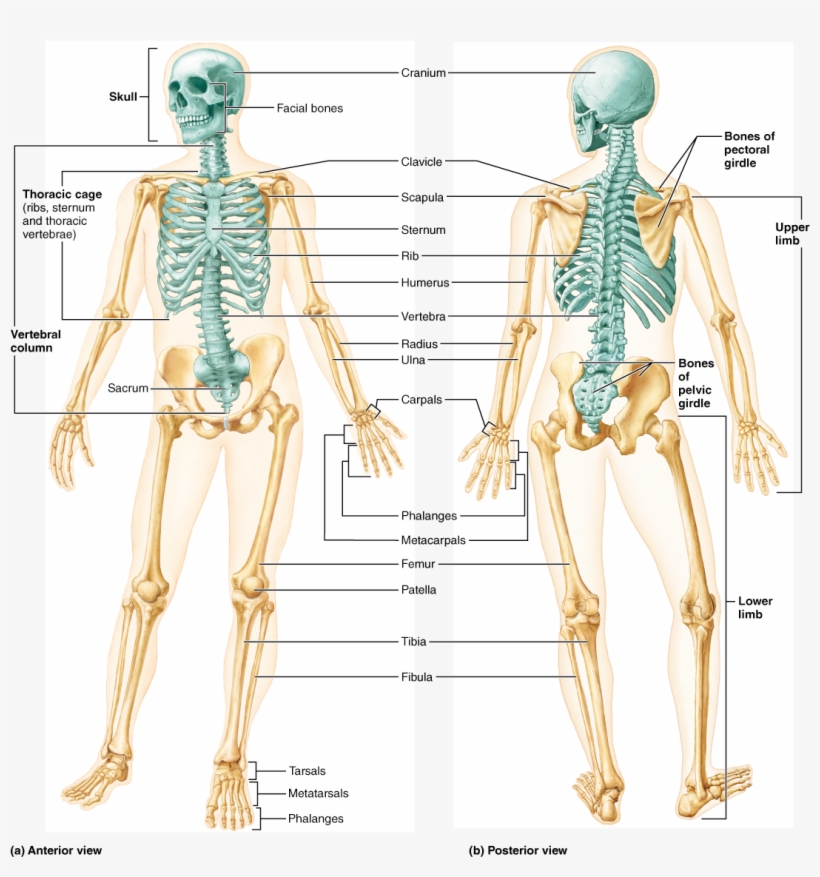
Bones, Part Human Skeleton Anterior And Posterior View PNG Image
The posterior view of the skeleton reveals bones that are obscured in the anterior view, most notably, the entire stack of individual vertebrae that span vertically from the sacrum to the skull.
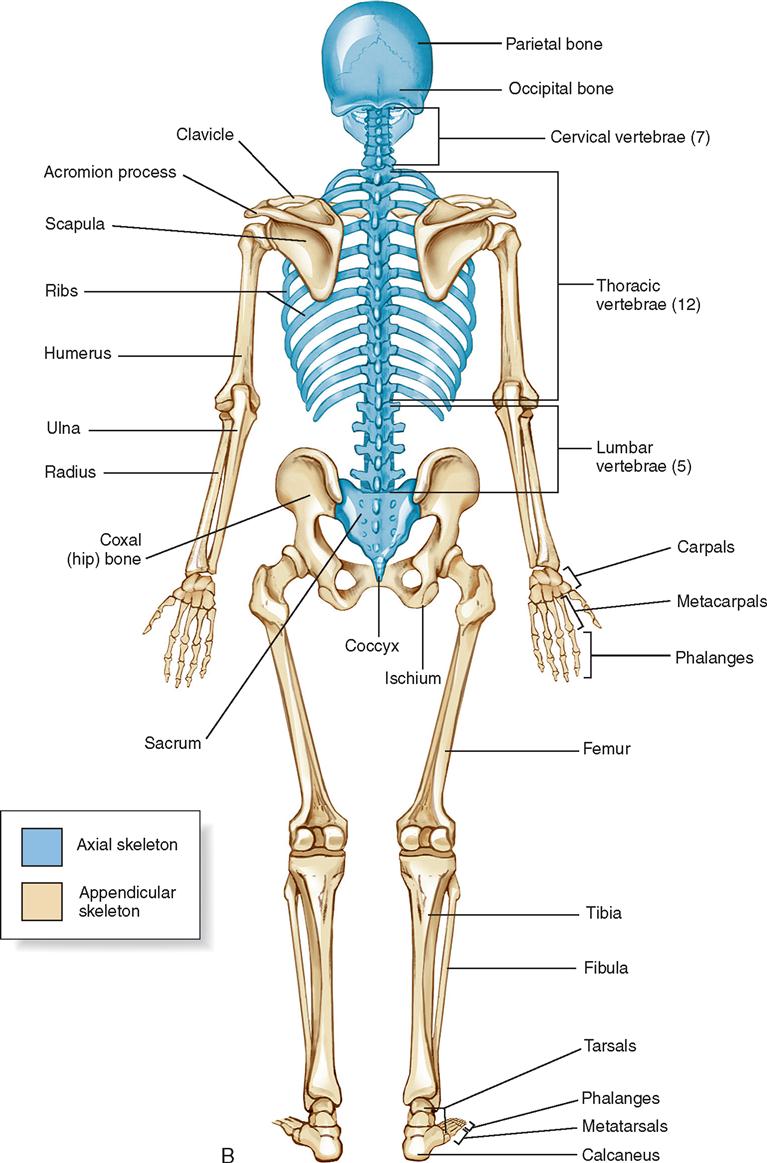
upper skeletal anatomy
1/20 Synonyms: none The posterior and lateral views of the skull show us important bones that maintain the integrity of the skull. The posterior surface protects the region of the brain that contains the occipital lobes and cerebellum .
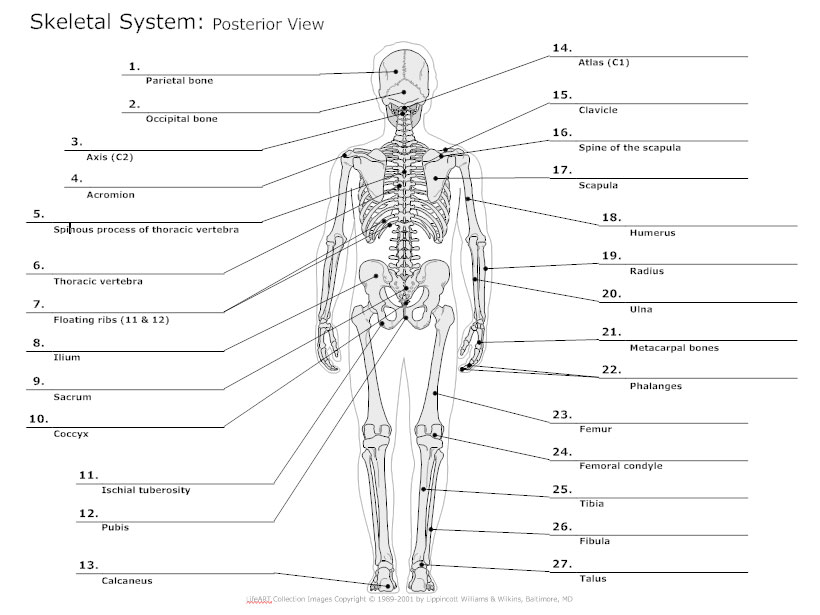
Skeletal System Diagram Types of Skeletal System Diagrams, Examples, More
The Skull Bones Anatomy - Inferior View. A number of cranial and facial bones are visible when viewing the skull inferiorly. Review the bones of the skull and test your knowledge. The Skull Bones - Orbital View. There are a number of markings on the cranial and facial bones which form the orbit of the skull.
Human Skeleton, Posterior View Photograph by Evan Oto Fine Art America
Lesser Trochanter Obturator Membrane Pelvis Posterior Sacroiliac Ligament Pubic Symphysis Pubofemoral Ligament Sacroiliac Joint Sacrospinous Ligament Sacrotuberous Ligament Sacrum Supraspinous Ligament Change Current View Angle Bones of the Pelvis and Lower Back (Posterior View) Toggle Anatomy System Cardiovascular System of the Lower Torso

Anterior and Posterior view Human bones anatomy, Body bones, Skeleton
This is the midline. Medial means towards the midline, lateral means away from the midline. The eye is lateral to the nose. The nose is medial to the ears. The brachial artery lies medial to the biceps tendon. Fig 1.0 - Anatomical terms of location labelled on the anatomical position.

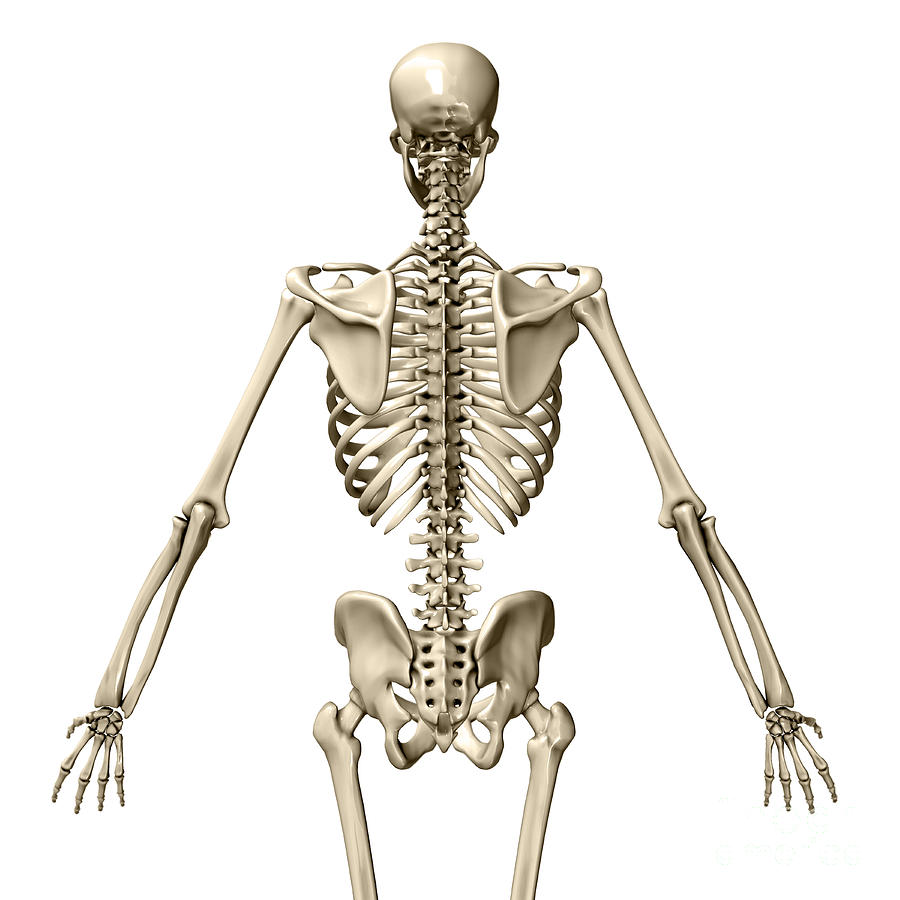
View of the Full Skeleton Posterior
posterior view See posterior view in : french | spanish parietal bone Flat cranial bone articulating with the frontal, occipital, temporal and sphenoid bones; the two parietal bones form the largest portion of the dome of the skull. lateral view of skull axis Second cervical vertebra supporting the atlas; it allows the head to rotate.
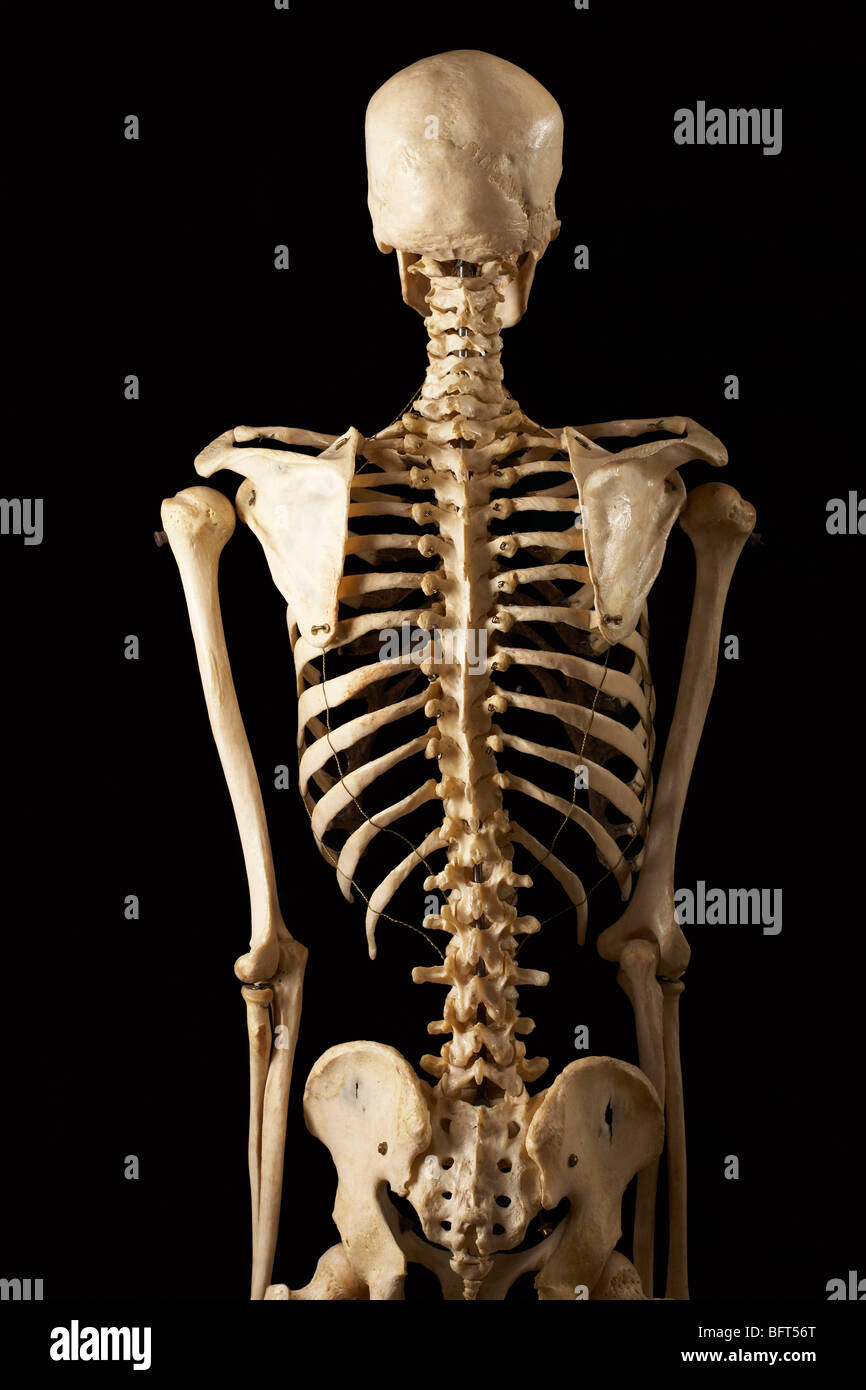
Posterior View of Skeleton Stock Photo Alamy
Browse 3,100+ posterior view of skeleton stock photos and images available, or start a new search to explore more stock photos and images. Sort by: Most popular. The skeletal system. The human skeletal system, vector illustrations of human skeleton front and rear view. Targeting back pain.
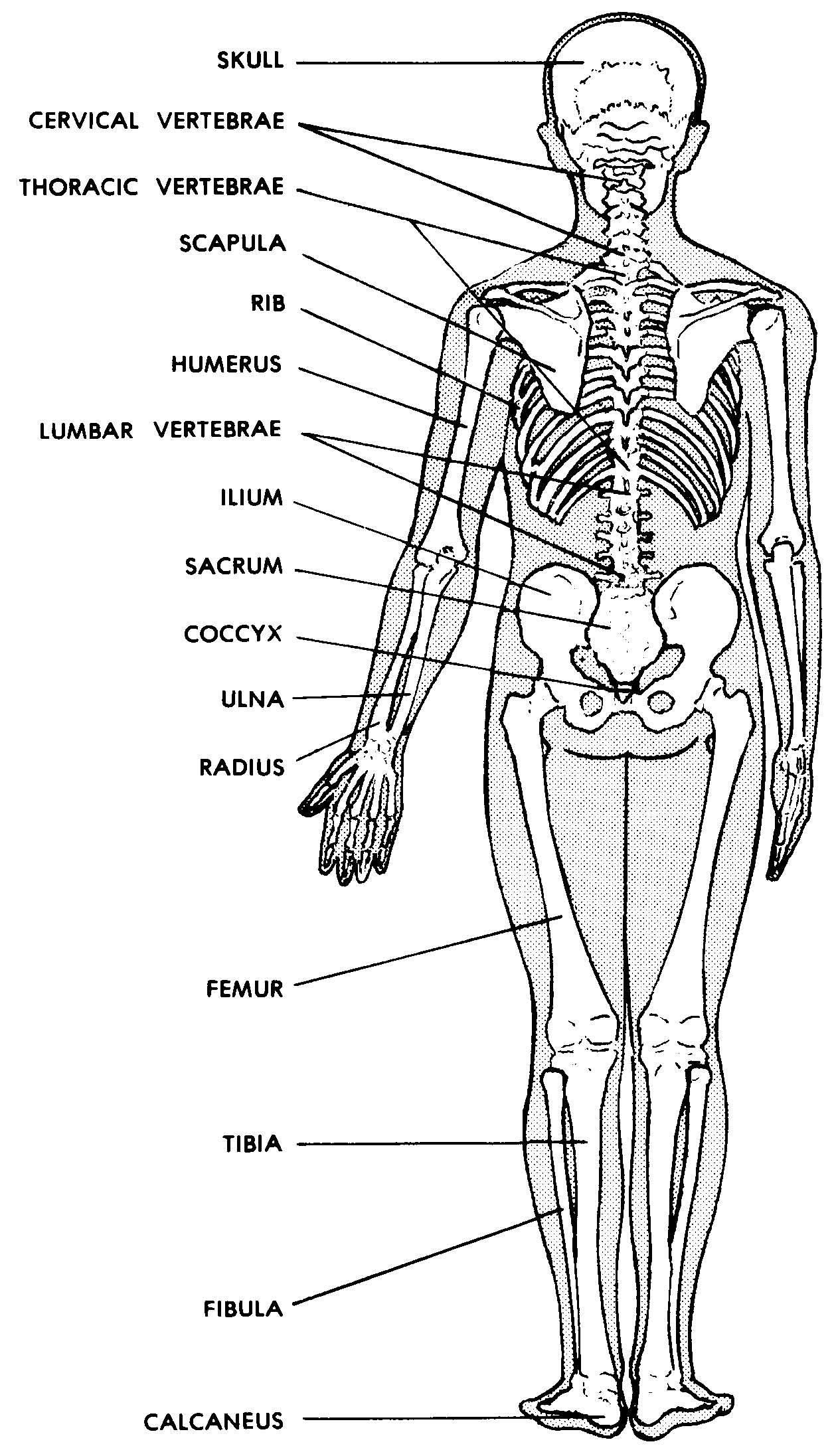
Images 04. Skeletal System Basic Human Anatomy
Figure 7.3.2 - Anterior View of Skull: An anterior view of the skull shows the bones that form the forehead, orbits (eye sockets), nasal cavity, nasal septum, and upper and lower jaws. Inside the nasal area of the skull, the nasal cavity is divided into halves by the nasal septum.
Posterior Anterior View
Skull 3 Lateral - Short - Medium - Text - Answers. Skull 4 Lateral - Short - Medium - Text - Answers. Skull 5 Lateral - Short - Medium - Text - Answers. Skull 6 Lateral - Short - Medium - Text - Answers. Skull 7 Lateral - Short - Medium - Text - Answers. Skull 1 Cranial - Short - Text - Answers. Skull 1 Inferior - Short - Medium - Long - Text.
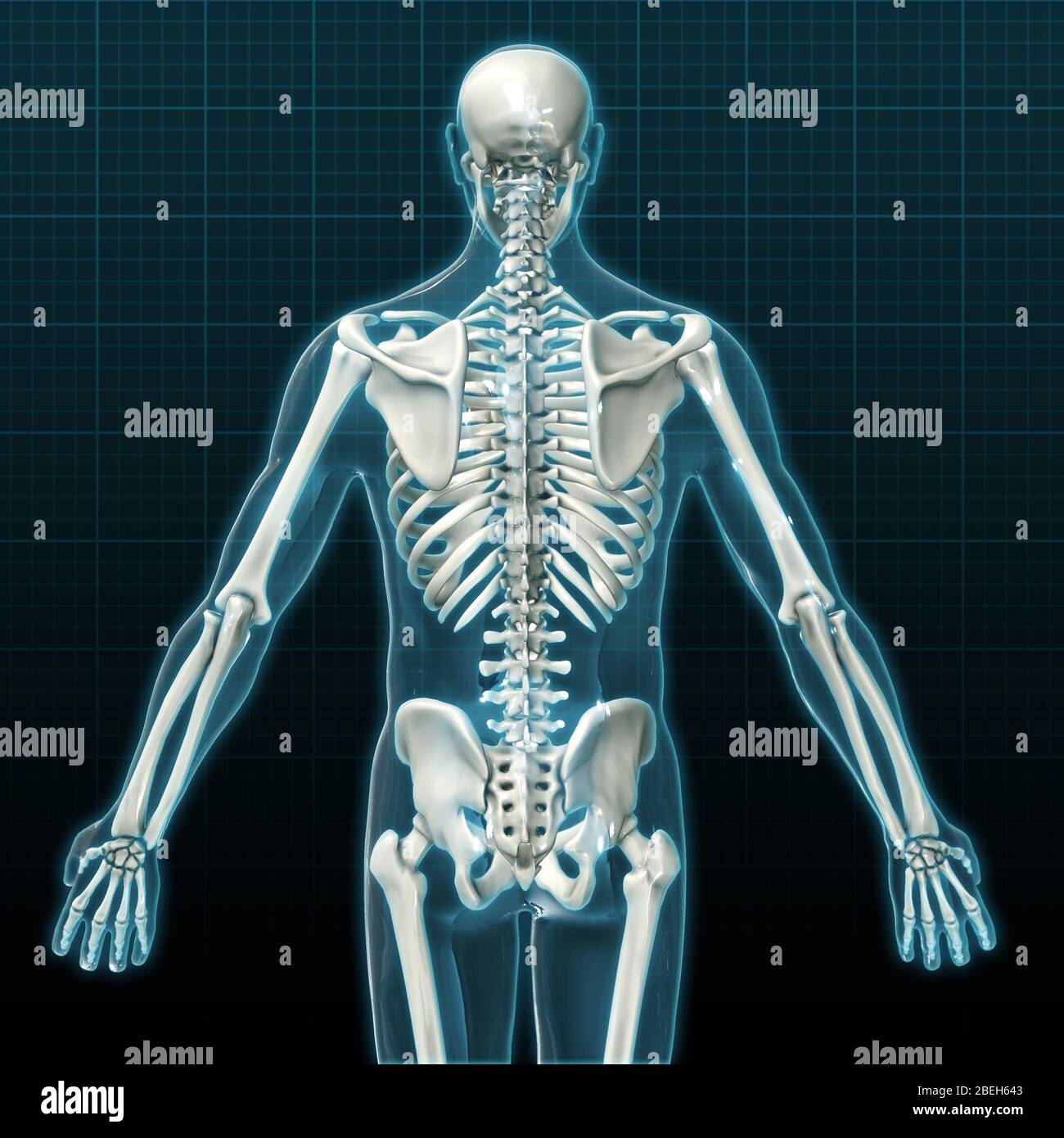
Human skeleton posterior view hires stock photography and images Alamy
posterior view. previous. next. gastrocnemius Large thick muscle forming the curve of the calf and allowing the foot to extend; it also helps the knee to extend. gracilis Muscle enabling the thigh to draw near the median axis of the body, and the leg to flex on the thigh and to rotate inwardly (toward the median axis). biceps of thigh.

skeleton posterior Real Bodywork
Figure 1.4.2 - Directional Terms Applied to the Human Body: Paired directional terms are shown as applied to the human body. is a two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has been cut. Modern medical imaging devices enable clinicians to obtain "virtual sections" of living bodies. We call these scans.

Human Skeleton From The Posterior View Didactic Board Of Anatomy Of
Dec. 24, 2023, 4:25 AM ET (Yahoo News) Human skeletons, remains of sharks, blood-sucking bats. human skeleton, the internal skeleton that serves as a framework for the body. This framework consists of many individual bones and cartilages.

lateral human anatomy
11.1 Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems ; 11.2 Naming Skeletal Muscles ; 11.3 Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck,. Figure 1.12 Regions of the Human Body The human body is shown in anatomical position in an (a) anterior view and a (b) posterior view. The regions of the body are labeled in boldface.
