
32 Label A Leaf Diagram Labels 2021
March 22, 2022 6.35 How does this align with my curriculum? Province/Territory Share on: Learn about the structure and function of the cells in leaves. Leaves are essential to life on earth. They can be tiny, like the leaves of the common water fern ( Azolla filiculoides), which are just one millimetre in length.
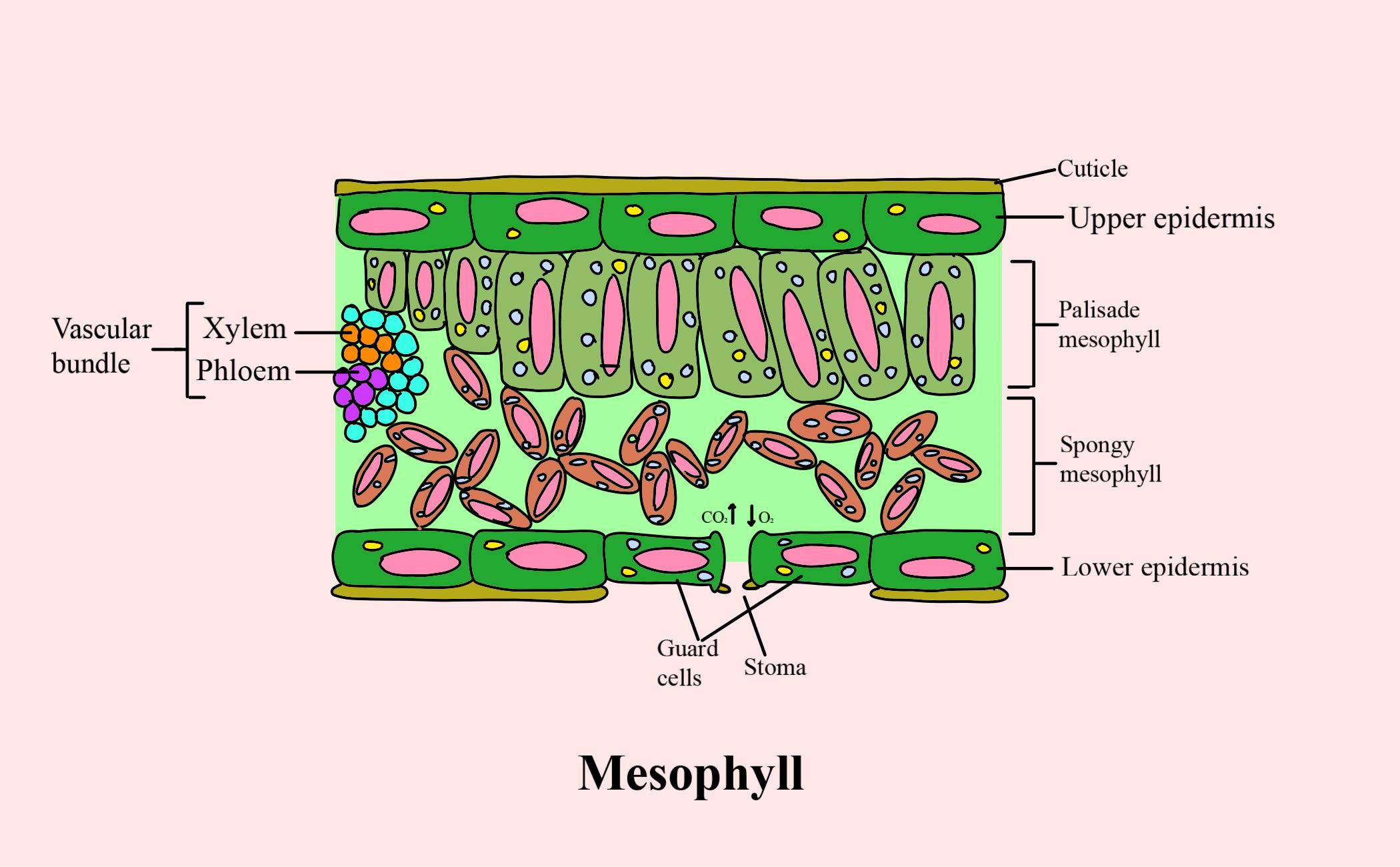
The mesophyll of leaf consists of (a) Spongy parenchyma cells (b) Palisade parenchyma cells(c
Distinguishing characteristics of a plant cell are its cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole. A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant. Plant cells, like all eukaryotic cells, contain a nucleus and other organelles, each with its distinct functions. However, plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from.

Leaf Structure photo Botany, Teaching biology, Biology
The air space found between the spongy parenchyma cells allows gaseous exchange between the leaf and the outside atmosphere through the stomata. In aquatic plants, the intercellular spaces in the spongy parenchyma help the leaf float. Both layers of the mesophyll contain many chloroplasts. Figure 30.10. 1: Mesophyll: (a) (top) The central.

PPT Chapter 32 Leaf Structure and Function PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1742285
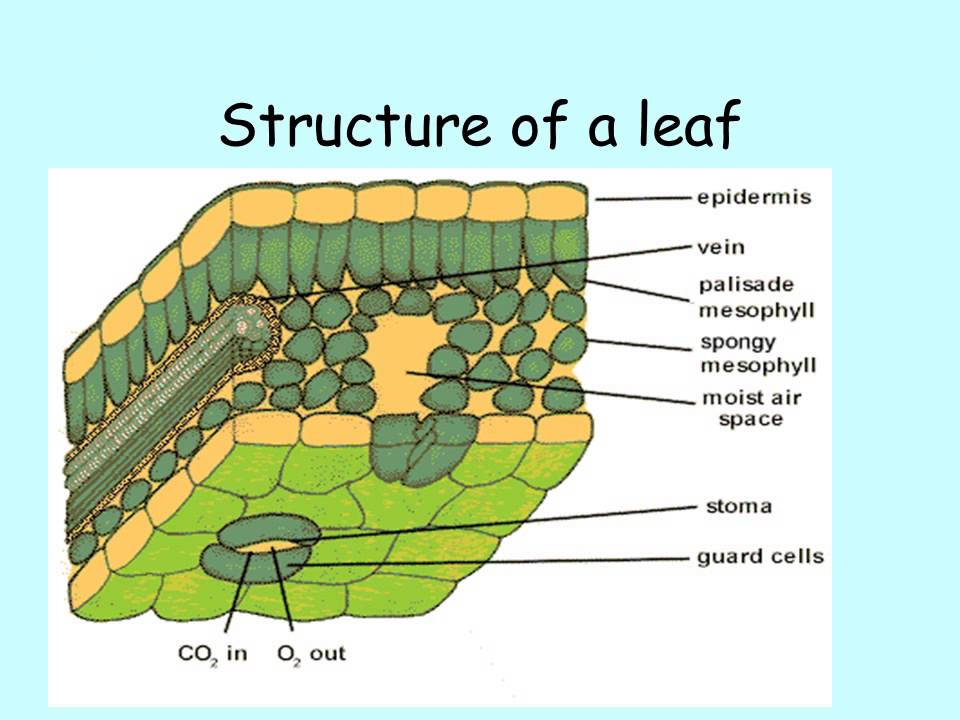
This type of plant is called a mesophyte (meso- meaning middle, -phyte meaning plant), preferring moderate climatic conditions. Figure 9.3. 1: Mesophytic Leaf. The outer layer of cells on both the upper and lower surface of the leaf is the epidermis. Can you find any pores (gaps) in the epidermis?

Internal Structure of a Leaf DanicateMullen
They are attached by a continuous vascular system to the rest of the plant so that free exchange of nutrients, water, and end products of photosynthesis (oxygen and carbohydrates in particular) can be carried to its various parts. Leaves are initiated in the apical bud (growing tip of a stem) along with the tissues of the stem itself.

Labeled diagram of a plant palisade cell where photosynthesis takes place Stock Photo Alamy
How do they work? An microphotograph of a stoma shows the two guard cells which regulate its opening and closure to limit water loss, excrete oxygen, and absorb carbon dioxide. The openings or pores in stomata are formed by two specialized sclerenchymal cells, the guard cells ( Figure above ).

Leaf & Chloroplast Structure photo Biology plants, Plant science, Teaching biology
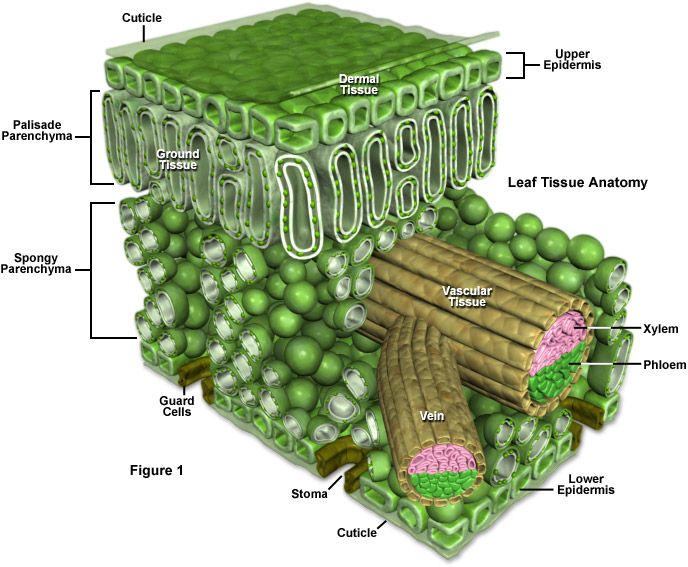
Like the stem, the leaf contains vascular bundles composed of xylem and phloem (Figure 3.4.2.6 − 7 3.4.2. 6 − 7 ). When a typical stem vascular bundle (which has xylem internal to the phloem) enters the leaf, xylem usually faces upwards, whereas phloem faces downwards. The conducting cells of the xylem (tracheids and vessel elements.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/leaf_crossection-57bf24a83df78cc16e1f29fd.jpg)
Plant bladeren en bladanatomie
Leaf Structure Under the Microscope ** Preparation, Requirements and Observations Introduction. Like any other multicellular living thing, leaf structure is made up of layers of cells. Viewing the leaf under the microscope shows different types of cells that serve various functions. Using a microscope, it's possible to view and identify these cells and how they are arranged (epidermal cells.

Plant Cell Labelled Diagram Ideas of Europedias
The table below describes the different structures in a leaf and their functions;. The specialised cells in leaves have adaptive features which allow them to carry out a particular function in the plant; Adaptations of Plant Leaves for Photosynthesis Table. You've read 0 of your 0 free revision notes Get unlimited access. to absolutely.
SC.912.L.14.7 Plant Structure to Dr. Suris Science Class!
Leaves are a part of the plant shoot system, which also includes stems and flowers . Key Takeaways Plant leaves are very important structures as they help to maintain life on earth by generating food (sugars) via photosynthesis. Leaves can have different shapes and sizes.

Photosynthates Biology I
Leaves are the main sites for photosynthesis: the process by which plants synthesize food. Most leaves are usually green, due to the presence of chlorophyll in the leaf cells. However, some leaves may have different colors, caused by other plant pigments that mask the green chlorophyll. The thickness, shape, and size of leaves are adapted to.

Leaf Structure, Types, Functions GCSE Biology Revision
Labeled diagram of plant cell. The typical characteristics that define the plant cell include cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin, plastids which play a major role in photosynthesis and storage of starch, large vacuoles responsible for regulating the cell turgor pressure. They also have a very unique cell division process whereby there is the.

dicot leaf anatomy
GCSE WJEC Structure of plants - WJEC Leaf structure Plants adapt in order to efficiently collect raw materials required for photosynthesis. These raw materials must be transported through the.
Leaf Structure and Photosynthesis YouTube
The structure of the umbrella tree leaf is typical of leaves in general (Above left photo). It has an outer layer, the epidermis, which produces a waxy waterproof coating. The epidermis of the undersurface produces guard cells, which swell and shrink to close and open the pores (stomata) which control the loss of water vapor (transpiration) and.

Cell structure of a leaf stock illustration Cell structure, Epidermis, Cell wall
A leaf cell, by definition, is any cell found within a leaf. However, there are many different kinds of leaf cell, and each plays an integral role in the overall function of the leaf and the plant itself. A single leaf cell may be designed to simply photosynthesize, or create sugars from the energy in light.

Pinus Leaf Cross Section Labeled
Figure \(\PageIndex{12}\): This image shows the same Elodea leaf cells again, this time with the cell wall, cell membrane, and tonoplast of one of the cells labeled. The cell walls are visible as thicker lines between the cells. The plasma membrane and tonoplast locations must be inferred. The plasma membrane is pushed against the cell wall.
